Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Cherry Red Spot

Introduction. Retinal artery occlusion (RAO) is an ophthalmological emergency and an important cause of acute vision loss with an incidence of 1 to 2 cases per 100 000 per year. 1 RAO is most commonly caused by embolus, thrombosis, or arteritis. It can cause partial or complete visual loss. 2 Without intervention, <20% of patients will have.
Retinal Artery Occlusion Optical Coherence Tomography Scans
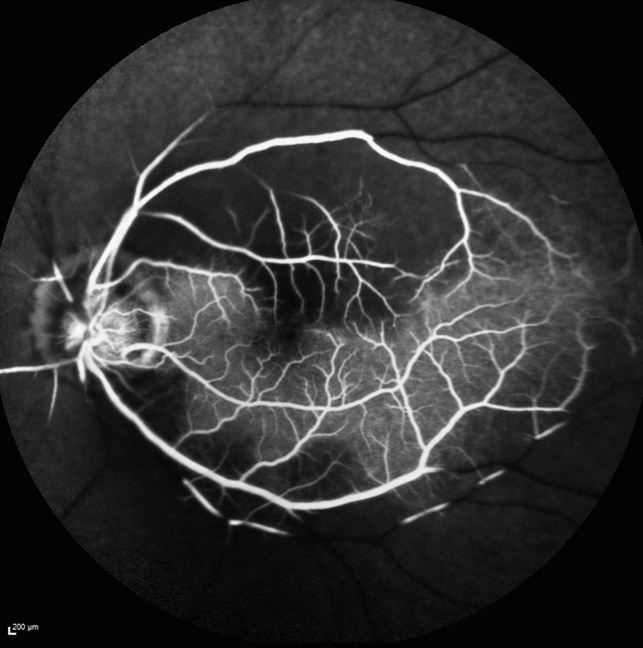
The central retinal artery supplies the inner retina and the surface of the optic nerve. In approximately 15 percent of individuals, it is assisted by a branch of the ciliary circulation, the cilioretinal artery, which may supply a portion of the retina, including the macula. This allows for preservation of vision in some patients with CRAO.
Anatomy Of Ocular Circulation A Central Retinal Arter vrogue.co

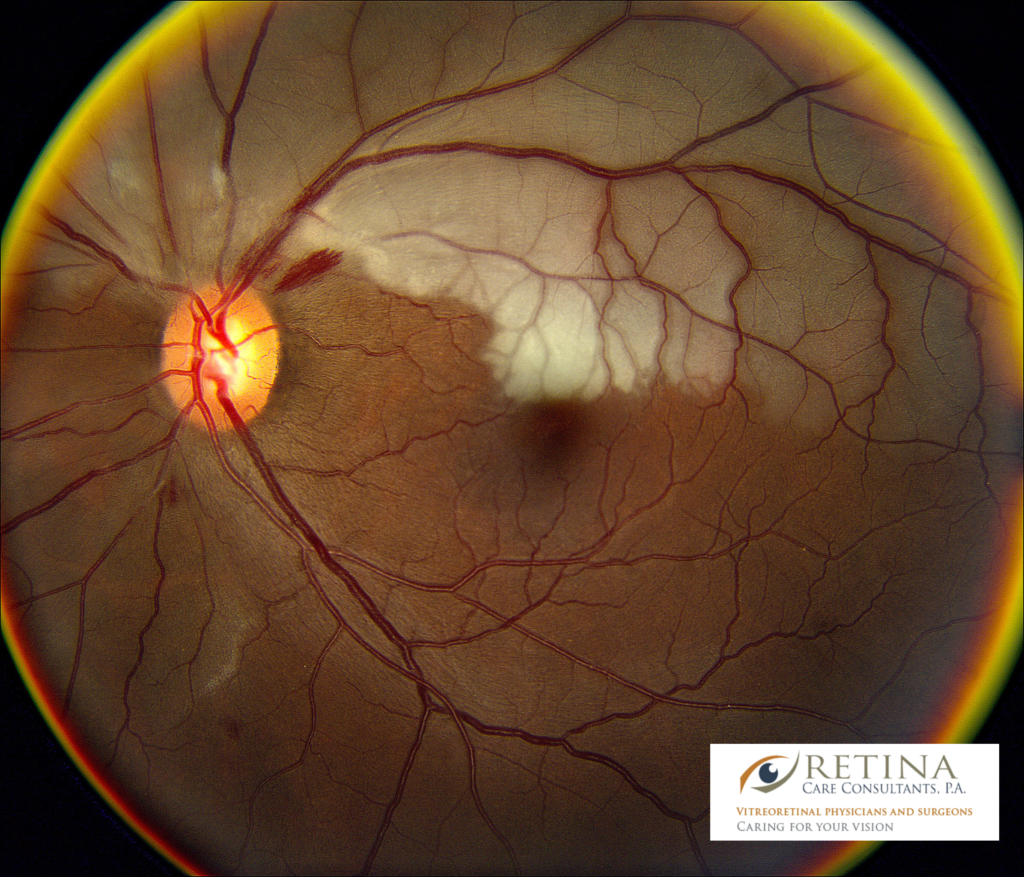
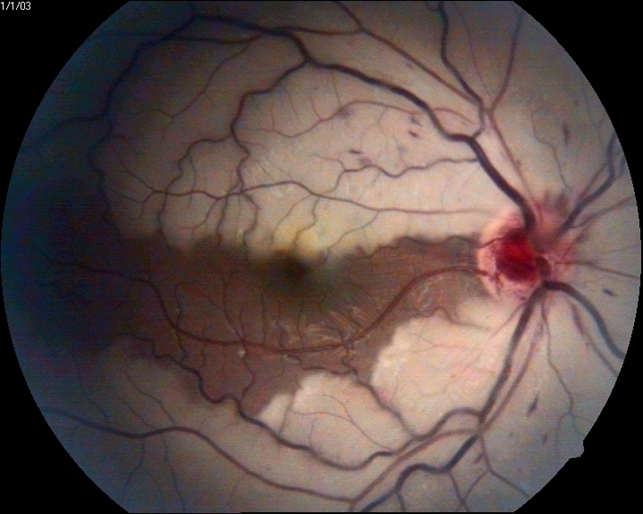
Introduction. Albrecht von Graefes first described central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) in 1859 as a disastrous ophthalmic emergency characterized by sudden onset, acute painless loss of vision, and a poor prognosis [].All cases of acute CRAO on fundus examination reveal extensive retinal whitening, presence of a cherry red spot, retinal vessel attenuation, and preservation of optic nerve.
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Vs Normal
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a form of acute ischemic stroke that results in painless vision loss attributable to retinal infarction.. (OCT‐A) to quantify retinal blood flow. OCT‐A uses OCT to differentiate between areas of tissue with erythrocyte movement and nonvascular tissue. 99 However, current OCT‐A.
Frontiers Inner Retinal Layer Hyperreflectivity Is an Early Biomarker for Acute Central
Abbreviations and Acronyms: CRAO ( central retinal artery occlusion ), KPNC ( Kaiser Permanente Northern California) Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a medical emergency representing an acute ischemic stroke that typically results in profound monocular vision loss. Patients diagnosed with acute CRAO may be offered numerous.
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Cilioretinal Sparing Fundus Fluorescein Angiography
To report a case of central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) after intravitreal injection of brolucizumab for a treatment-naïve neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) patient without comorbid cardiovascular disease history. A 79-year-old Asian male without a cardiovascular disease history such as diabetes or hypertension underwent three times of monthly consecutive intravitreal.
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Oct

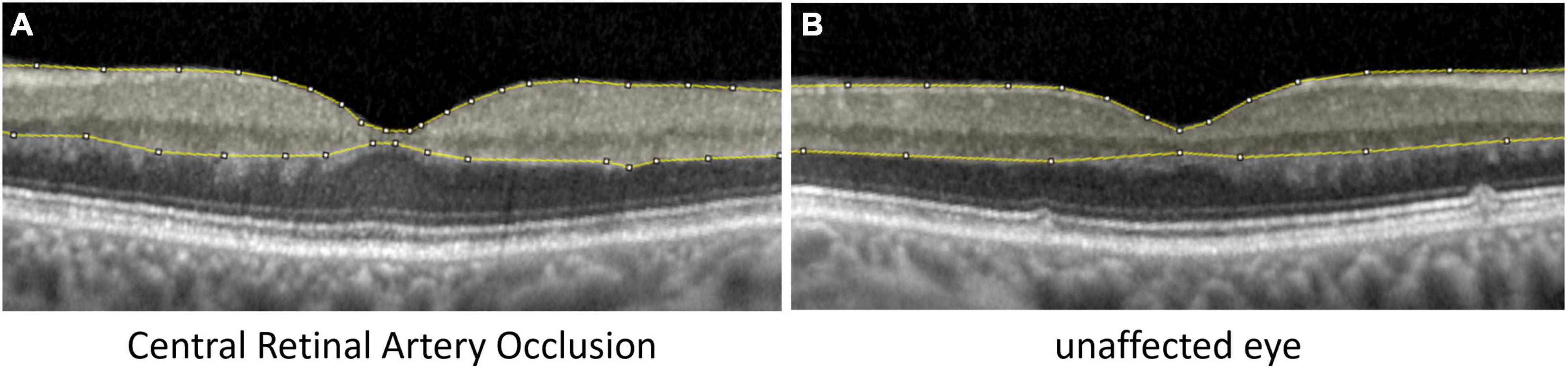
This article describes optical coherence tomography (OCT) findings in patients with central retinal artery occlusion by conducting a retrospective review of two cases. Central retinal artery occlusion shows a distinct pattern on OCT images. In the acute phase, OCT images demonstrate the increased reflectivity and thickness of the inner retina.
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Retina Image Bank A
The most common is the embolic occlusion of the central retinal artery or branch retinal arteries via remote embolization from the ipsilateral internal carotid artery, aortic arch, or heart. This assertion is based on a study of 234 patients with nonarteritic CRAO; 85% had cervical vessel imaging performed, and 71% of these had ipsilateral carotid plaque.
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion CRAO Geeky Medics
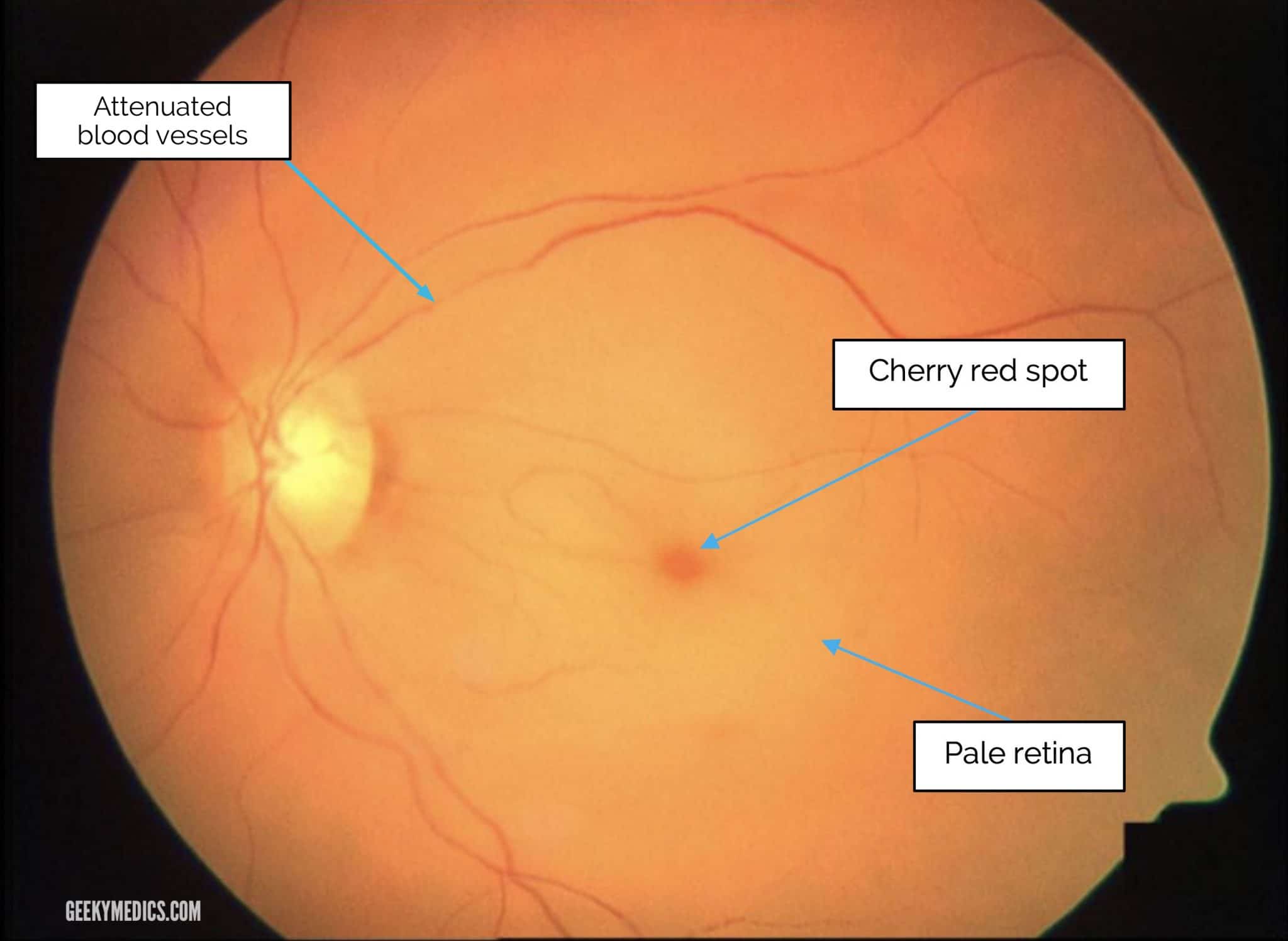
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is an ophthalmic emergency that presents as painless, sudden and typically severe monocular vision loss. 1. Historic treatment options for patients diagnosed with CRAO mostly involve attempts to either reduce intraocular pressure, improve oxygenation, or dislodge the embolus. 2.
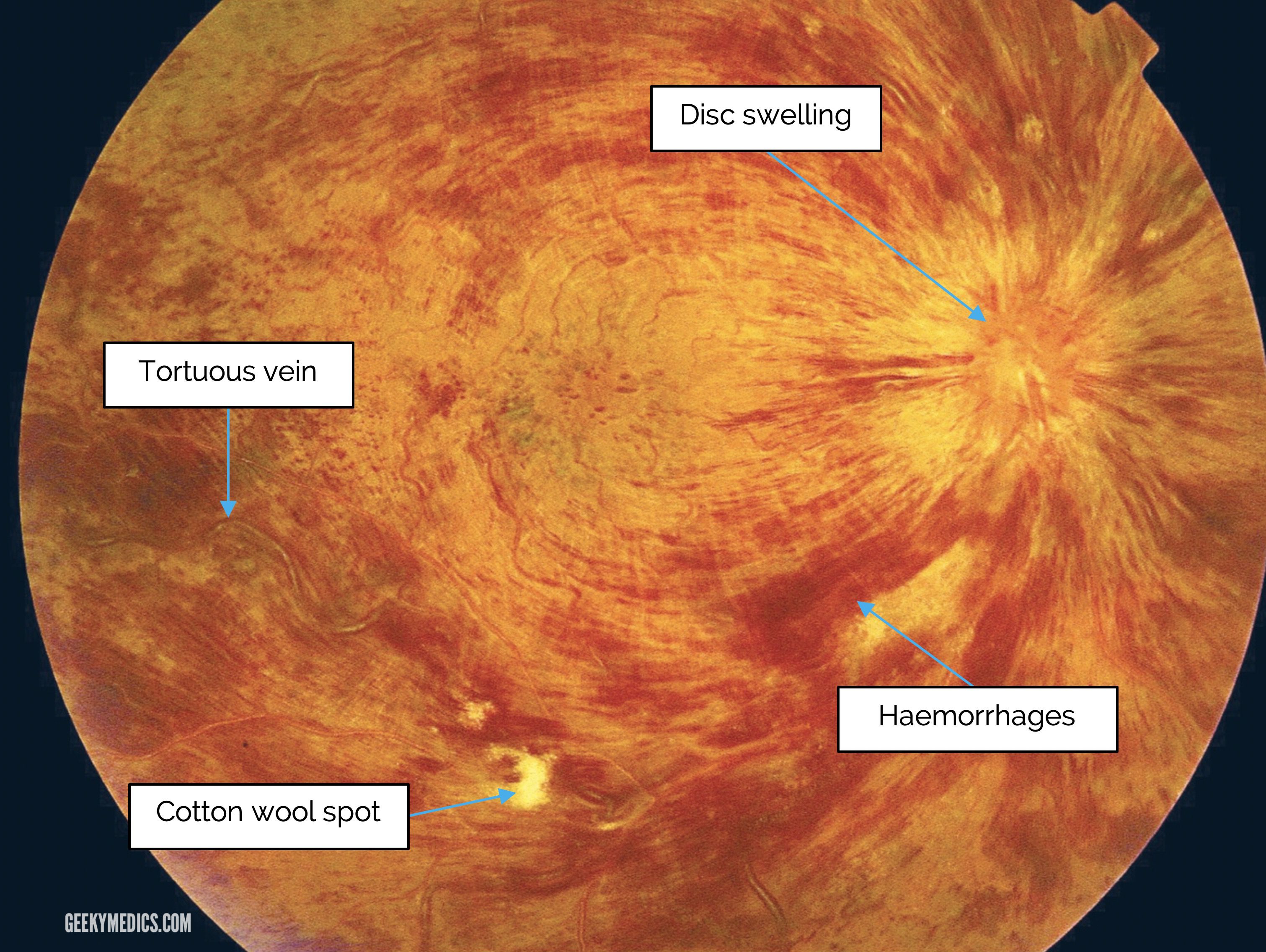
Fundoscopic Appearances of Retinal Pathologies Geeky Medics
Aims: To report spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) findings in cases of impending or occult central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) in which a diagnosis other than CRAO was made on initial presentation.Methods: Retrospective, observational case series of patients diagnosed with CRAO for whom on initial presentation fundal examination and OCT findings were deemed unremarkable.
Acute central retinal artery occlusion, left eye. (a) Fundus... Download Scientific Diagram

entral C retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is an oph-thalmic emergency characterized by vision loss attributable to obstruction of blood flow through the central retinal artery (CRA), 1 of the major arteries supplying blood to the eye. CRAO can be categorized into 4 distinct subtypes that can differ in cause, clinical presentation, and treatment.
Central retinal artery occlusion. Notes (A) Color fundus photograph... Download Scientific

Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO), like a stroke in the brain, is a critical eye condition that requiring urgent medical attention.. Parmar Y, Prabhu V, et al. Retinal OCT findings in.
Clinical Utility of OCT Angiography for Retinal and Choroidal Vascular Diseases Retina Today
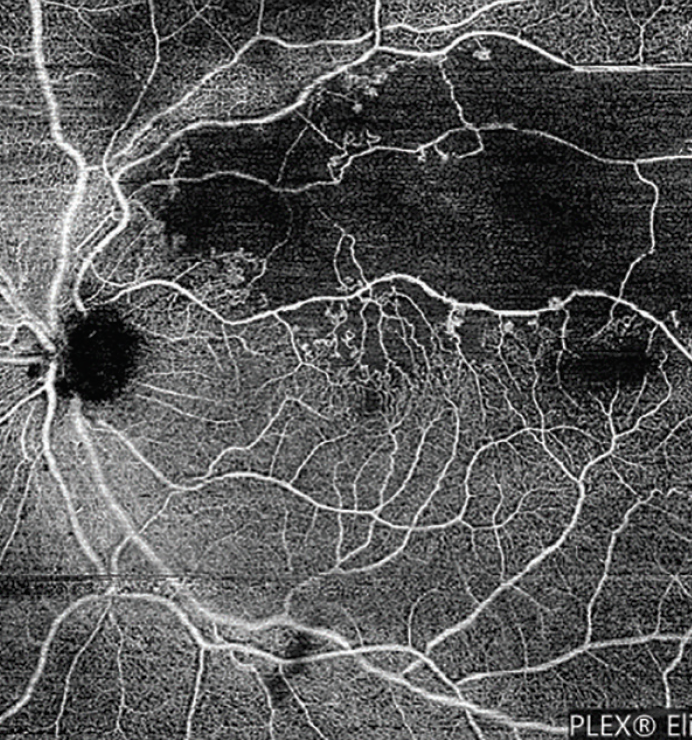
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is an ocular emergency. Patients typically present with profound, acute, painless monocular visual loss—with 80% of affected individuals having a final visual acuity of counting fingers or worse. CRAO is the ocular analogue of a cerebral stroke—and, as such, the clinical approach and management are.
Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion Brao Optical Coherence Tomography Scans My XXX Hot Girl
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a rare event with an age and sex adjusted incidence of 1.9 per 100,000 people in the United States. 1 An analysis of claims data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service demonstrated a similar incidence rate for CRAO of 1.8 per 100,000 person-years. The authors noted an increasing rate of CRAO.
Management of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Scientific Statement From AHA
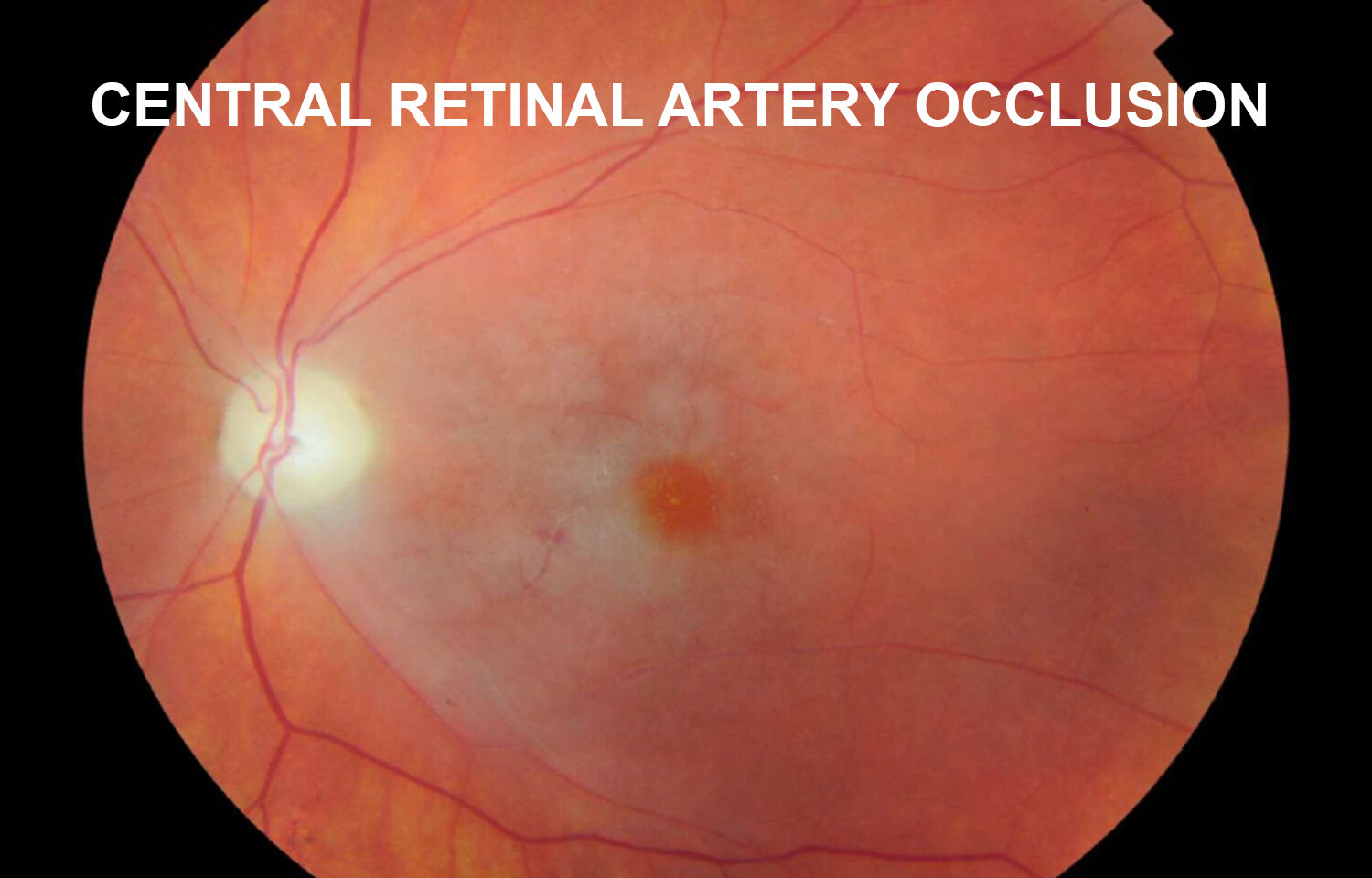
Purpose To study the optical coherence tomography (OCT) changes in eyes with acute central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) of different severity and at different disease stages. Methods The study included acute CRAO cases of < 7 days duration, imaged on OCT at various time points. Based on the OCT findings at presentation, cases were classified into three severity groups: mild, moderate, and.
Vasculopathie en OCT
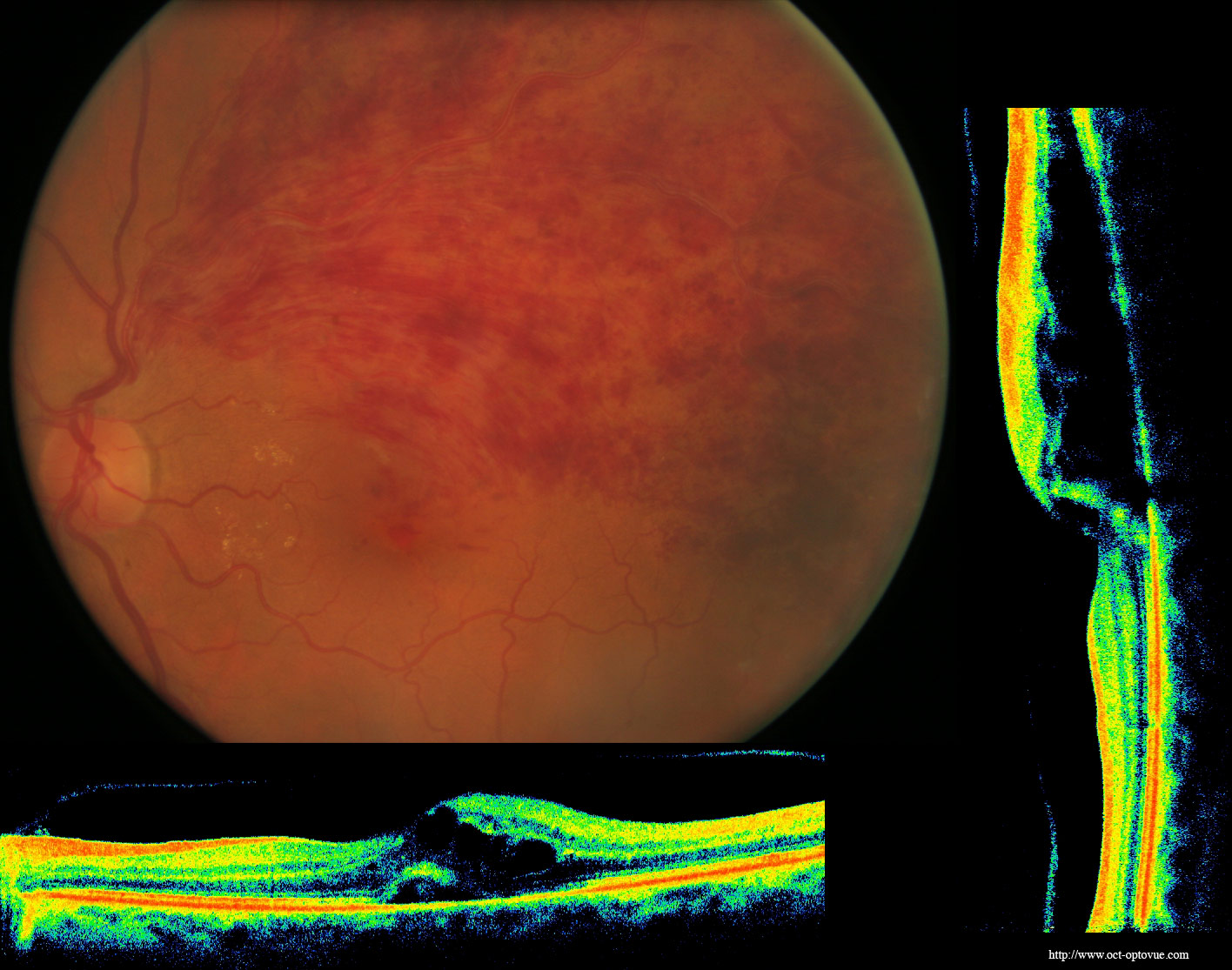
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is an ophthalmic emergency which is analogous to a cerebral stroke. It is caused by the sudden blockage of the central retinal artery (CRA) and usually presents as sudden, painless monocular vision loss. The incidence of CRAO is estimated as 1 in 100,000 patients per year and 1 in 10,000 outpatient visits.